Locations
- San Francisco
- Sunnyvale
- Palo Alto
- San Mateo
- San Jose
- Milipitas
- Seattle
- Walnut Creek

An autoimmune disease occurs when the body’s immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 types of autoimmune disorders.
A person may have more than one autoimmune disorder at the same time. Common autoimmune disorders include:
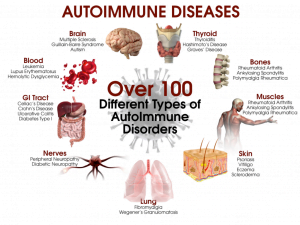
Symptoms may vary, based on the type and location of the faulty immune response. Common symptoms include:
Symptoms vary depending on the disorder and the part of the body affected. Some autoimmune disorders affect certain types of tissue throughout the body—for example, blood vessels, cartilage, or skin. Other autoimmune disorders affect a particular organ. Virtually any organ, including the kidneys, lungs, heart, and brain, can be affected. The resulting inflammation and tissue damage can cause pain, deformed joints, weakness, jaundice, itching, difficulty breathing, accumulation of fluid (edema), delirium, and even death.
Autoimmune reactions can be triggered in several ways:
Why something triggers an autoimmune reaction or disorder in one person (and not another) is usually unknown. However, heredity is sometimes involved. Some people have genes that make them slightly more likely to develop an autoimmune disorder. This slightly increased susceptibility to an autoimmune disorder, rather than the disorder itself, is inherited. In susceptible people, a trigger, such as a viral infection or tissue damage, may cause the disorder to develop.
While there is no magic cure for autoimmune diseases, there are ways of boosting the immune system to reduce the severity of symptoms and possibly prevent an outbreak or flare-up. Rev(IV)al Hydration’s Autoimmune Drip formula works alongside your other doctor approved treatments for whole-body immunity support.
This treatment has a 100% absorption rate by the body because it bypassed the digestive system and delivered directly to the cells. This is important because vitamins and supplements taken orally are not as potent as Rev(IV)al Hydration’s methods. Below we will examine the vitamins and minerals that go into each blend of Autoimmune Drip and how they help to boost the immune system.
Vitamin B12
B12 plays a vital role in the body, helping white blood cell production, which is essential for a properly functioning immune system. Certain autoimmune diseases stop the body from absorbing vitamin B12 in the stomach, which can further complicate health issues. Luckily, because IV infusions bypass the stomach, the body can absorb the vitamins it needs.
Glutathione
Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that is important in minimizing damage to the body from oxidative stress. Glutathione is especially important for those suffering from autoimmune diseases because it protects cells from inflammation, boosts the immune system, and supports the healing of the stomach lining and the blood-brain barrier. An IV infusion of glutathione is the most effective method for increasing levels stored in the body.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is also known to be a potent antioxidant and supports the body by playing a role in cellular functions. By helping the immune system, it calms the body’s natural response so the body can destress. Stress can exacerbate autoimmune symptoms and make it more challenging for the body to defend itself from other external factors, like viruses. In lab studies, IV therapy of vitamin C for autoimmune diseases has shown effective in helping to manage symptoms.
L-glutamine
L- glutamine also supports the health of the stomach lining and can be especially helpful for those suffering from leaky gut or other stomach related autoimmune diseases. Having adequate levels of L-glutamine can help heal the gut, improve brain health, and support muscle repair. It is an essential amino acid in maintaining optimal health for those suffering from autoimmune diseases.
Magnesium
Micronutrient deficiencies in the body, specifically magnesium, selenium, and zinc, are linked to several autoimmune diseases. This is thought to be because all three of these nutrients help to regulate inflammation in the body. During periods of inflammation, the body is not absorbing all the nutrients it should be from food and supplements. Specifically, autoimmune thyroid disorders like Hashimoto’s disease can benefit significantly from additional magnesium supplements.
Selenium
Selenium is another helpful tool for managing inflammation because it is an essential trace mineral that has anti-inflammatory effects in the body. In a study published in 2019, it was demonstrated that an adequate quantity of selenium in the body could contribute to the management of complications of autoimmune diseases and even improved quality of life in patients with autoimmune diseases. IV treatments are so effective because it detours around the stomach for maximum absorption and potency. This mineral is also known for being particularly helpful with improper thyroid function.
Zinc
Zinc is the second most abundant metal in the body and is involved in cell division and growth, DNA and RNA transcription, and vitamin and mineral absorption. This is another mineral that deficiency is linked to autoimmune disorders; this is because it is essential in the production of white blood cells. White blood cells are the cells that make up the immune system! Since zinc is one of the 24 crucial minerals that the body cannot store or make, it is vital to supplement your intake. It has also been shown to be a helpful mineral for those suffering from leaky gut or other autoimmune disorders affecting the gut.
Blood tests that indicate the presence of inflammation may suggest an autoimmune disorder. Such tests include the following:
The goals of treatment are to:
The services provided by us have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. The material on this website is provided for informational purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult your physician before beginning any therapy program. Any designations or references to therapies are for marketing purposes only.
© 2024 Revival Hydration. | All Right Reserved | Terms And Conditions